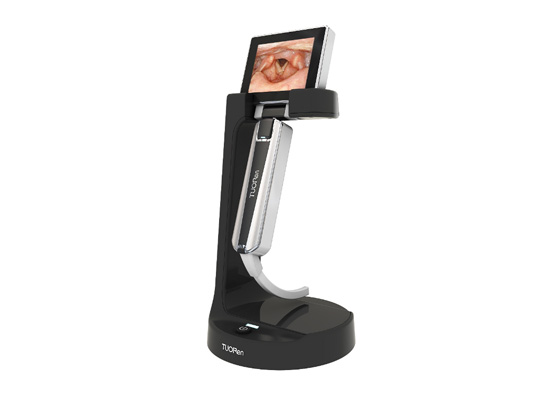
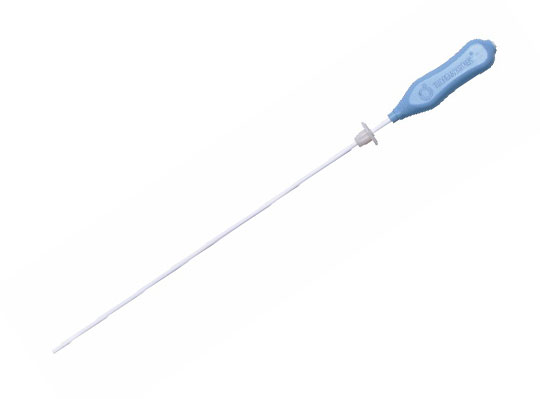
Indirect laryngoscope is mainly used to observe the structure of epiglottis, glottis, vocal cords and so on. When doing this examination, there may be a sense of nausea in the pharynx. It is necessary to spray the surface anesthetic to pharynx. The indirect laryngoscope is only the doctor's eye with a similar reflector in his hand. The deep lesions can not be seen.
(1) every place in the larynx should be checked in turn, before, before, left, right, up and down. Attention should be paid to congestion, swelling, hyperplasia and ulceration. If there is vocal cord dyskinesia, we should pay attention to whether there are tumors in the laryngeal or subglottic region, the arytenoid joint disease or the vocal cord paralysis. The retention of saliva in the pyriform fossa may be caused by posterior ring tumor, upper esophageal tumor, foreign body or pharyngeal paralysis. Interarytenoid superficial ulcers or granulation rare laryngeal tuberculosis patients.
(2) for patients with short tongue thickness, short tongue tie, long epiglottis or infantile type, it is often difficult to check. Children's examination is also not easy to succeed. Lesions at the anterior commissure of the larynx are easy to be ignored. A direct laryngoscopy should be performed in all patients who can not be identified by laryngoscopy.
(3) see the image in the indirect laryngoscope for laryngeal image, is shown in front of the rear mirror throat is the throat, but not upside down.
(4) in the larynx, the image is oval. The vocal cords, glottis and other tissues are all 2/3 in length. The color of the throat mucosa is related to the intensity of the incoming light. Strong light often makes the color of the congestive mucosa normal or shallower.
Tel:0373-8100637